
Today, the worlds of security and business, as well as our daily lives, are driven by the latest technology.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most widely used advances. However, there are other tools that, by joining forces with branches of AI, such as machine learning or deep learning, can empower any action for which it has been programmed even further.
One of them is the Internet of Things (IoT), a powerful network of devices that constantly captures large amounts of information for various purposes, be they statistical, commercial, protection, etc. When instructed by Artificial Intelligence algorithms, the Internet of Things is able to process all the information it receives in a more organized way, learn from past decisions, predict future consequences and make better decisions, becoming, thus, an Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT). Here, we tell you all about it.
- What is IoT?
- What is AI?
- How can IoT and AI support each other?
- Benefits of AI and IoT
- Examples of AI and IoT
- The future of AI and IoT
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things is a whole system of physical devices that receive and transfer data over wireless networks with minimal human intervention.
It is, then, elements such as digital assistants, speakers, lighting, sensors, and other gadgets with applications that connect to the Internet, receive specific information from the real world, and respond to it through determined actions.
A common example is a sensor that turns on lights when activated. We also find applications for financial transactions or controls that allow entry to certain people, vehicles, or shipments.
The part of the IoT that triggers responses to incoming data or conditions is known as a control loop. Some control loops perform their processing and response tasks simply. But others require more complicated rules to tie together insights and answers since collecting a multitude of data sometimes makes it difficult to process and analyze them. This is where AI comes in.
If you want to learn more about IoT and all its applications, read our article here.
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the combination of algorithms in a machine aimed at having it interpret certain conditions and, based on this, make decisions; this is done in a manner very similar to the functioning of the human mind and, like the Internet of Things, with minimal human intervention.
There are three forms of Artificial Intelligence that we use in multiple aspects of our lives and that both public and private industries also implement in their most important operations:
Rule-based or simple AI: This is software with programmed rules set up to link information with decision-making.
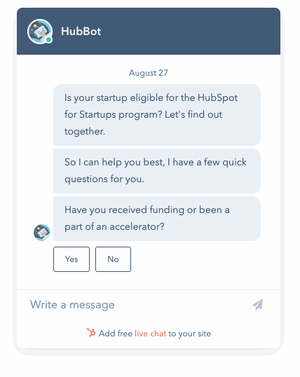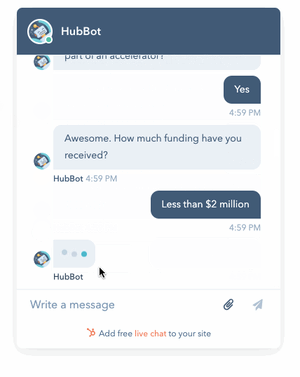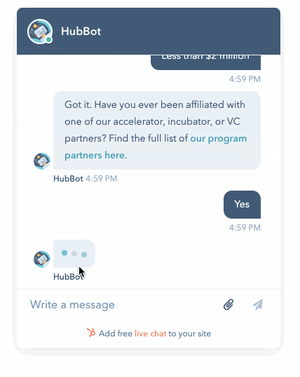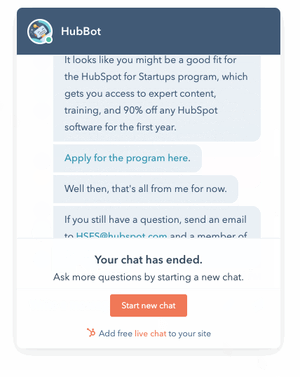
Credits: Hubpsot
Neural networks or inferences: In these cases, AI builds a sort of engine that, by imitating the mental activity of people, responds to triggers from inferences or data contained in voluminous databases. Today, this technology is used in image analysis, facial recognition, and video surveillance.

Machine Learning (ML): This is a branch of Artificial Intelligence in which a machine learns a certain behavior over time rather than being programmed for it from the beginning. This type of learning can consist of monitoring systems and relating events to responses or actions that a device's memory will collect eventually. Deep learning, in turn, is a type of machine learning that trains a computer to learn on its own from pattern recognition.
Netflix movie recommendation | Credits: Label your data
Learn more about the different types of AI in our article here.
How can IoT and AI support each other?
Strictly speaking, every IoT application uses AI from the moment it integrates software to respond to a triggering event. Rather, the real link between the two technologies happens when AI trains the IoT in its analysis stage to more accurately detect the data and requests it receives from the real world. Thus, when the IoT receives data, AI empowers it to decipher the context of a request and make more informed decisions.
The fusion between IoT and AI, or Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT), provides solutions such as:
- Collect, manage and analyze data to extract the most valuable insights.
- Enable fast and effective analysis.
- Ensure security against cyber-attacks.
- Strengthen data privacy and user confidentiality.
- Handle centralized and localized intelligence requirements.
In the case of rule-based or simple AI fusion, a programmer uses tables containing a limited number of states or events, describes them, and shows IoT devices the consequences or specific ways to react to them.
For example, imagine a worker entering a warehouse with shipped goods. Using AIoT, this person could turn on the light by pressing a certain switch, a precise response but one that can only happen through very timely action.
The incorporation of Machine Learning, on the other hand, would expand the possibilities even further, as it could teach the IoT units to collect and identify, over time, as much information as possible about situations in which it is necessary to turn on the light, without the need for a worker to flip the switch. In this way, it would be enough to mention phrases such as "I need more light" or "It's dark" for the AIoT to meet these requirements.
Benefits of AI and IoT
The IBM Institute interviewed a group of C-suite executives. Of these, 19% commented that they prioritize the fusion between IoT and AI because of the many business benefits it gives them in return, such as intelligent automation, personalized experiences, and proactive engagements. Some of the most popular benefits of this alliance, for both businesses and consumers, include the following:
Operational efficiency:
IoT and AI constantly monitor data streams and can detect patterns that would escape the study of experienced analysts. In turn, machine learning detects parameters that can be modified, and thus, users are shown which operational processes or activities are unproductive and take up too much time. Companies like Google often do this to reduce costs in their data centers.
Product and service innovation:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has enabled people to communicate through devices. AIoT can improve new or existing products and services by achieving better data processing and analytics. For example, Rolls Royce is already using this technology to deploy IoT-enabled airplane engine maintenance amenities.
Enhanced risk management:
AI and IoT employ data to predict risks that can affect the movement of markets. In this way, they can prevent these problems with an appropriate response. This protects the integrity of employees, reduces financial losses, and prevents cyber-attacks.
Examples of AI and IoT
Now, let's take a closer look at some applications that result from the union between AI and IoT:
Robots in manufacturing:
Manufacturing has long relied on AIoT to speed up its processes. The robots used in manufacturing plants contain implanted sensors that enable data transmission. In addition, these tools also have AI algorithms that constantly display important new information for them. This way, it is possible to save costs and time and improve the manufacturing process over the years.

Intelligent Retail:
Most retail stores are equipped with camera systems with the highest computer vision and use facial recognition to identify customers entering the stores. Thanks to AI capabilities, it is possible to detect and categorize specific traits of each person that will inform future operational and marketing decisions. Some of these aspects regarding customer behavior are product preferences, gender, age, and much more. Thus, decision-makers could deploy ads that target a certain demographic group or streamline the entry process for shoppers.

Intuitive automotive sector:
The automotive industry turns to various AIoT applications to ensure the reputation and safety of its vehicles, such as maintenance and assembly. AI tools are able to predict if any part of a vehicle is going to fail by combining different data from workshops, safety agencies, and others to see which components might need to be replaced or overhauled. One of the most notable examples in this sector is autonomous cars that can predict the behavior of drivers and pedestrians, as well as determine road conditions, weather, and ideal speed.

The future of AI and IoT
The future looks quite promising for IoT and AI, especially when they work together as we have seen. A recent survey on technology trends by SADA System revealed that AIoT is the most popular technology tool today and that companies are investing more than ever. It is believed that this will only increase.
Like every advancement of our time, AIoT also faces significant challenges. One of them is the case of inference-based AI, which requires much more complex software to collect data and define inference rules. It will be interesting to see companies betting on the investment of more developed software in order to strengthen processes such as product movement and the operational efficiency of factory personnel.
As for other outcomes that we can expect in the near future, there is a reduction of human intervention in operations, but not its disappearance. It is expected that company employees will now participate in their decisions in a much more informed way thanks to AIoT.
Thus, an exciting era of breakthroughs that will transform businesses and industries around the world awaits us. On the one hand, the IoT, which provides AI with the data it needs to keep working, and in turn, AI, trains the IoT and teaches it to discern between multiple possibilities. It is a perfect match between human analytics and inquiry.
Learn more about intelligent systems and all their implications here.