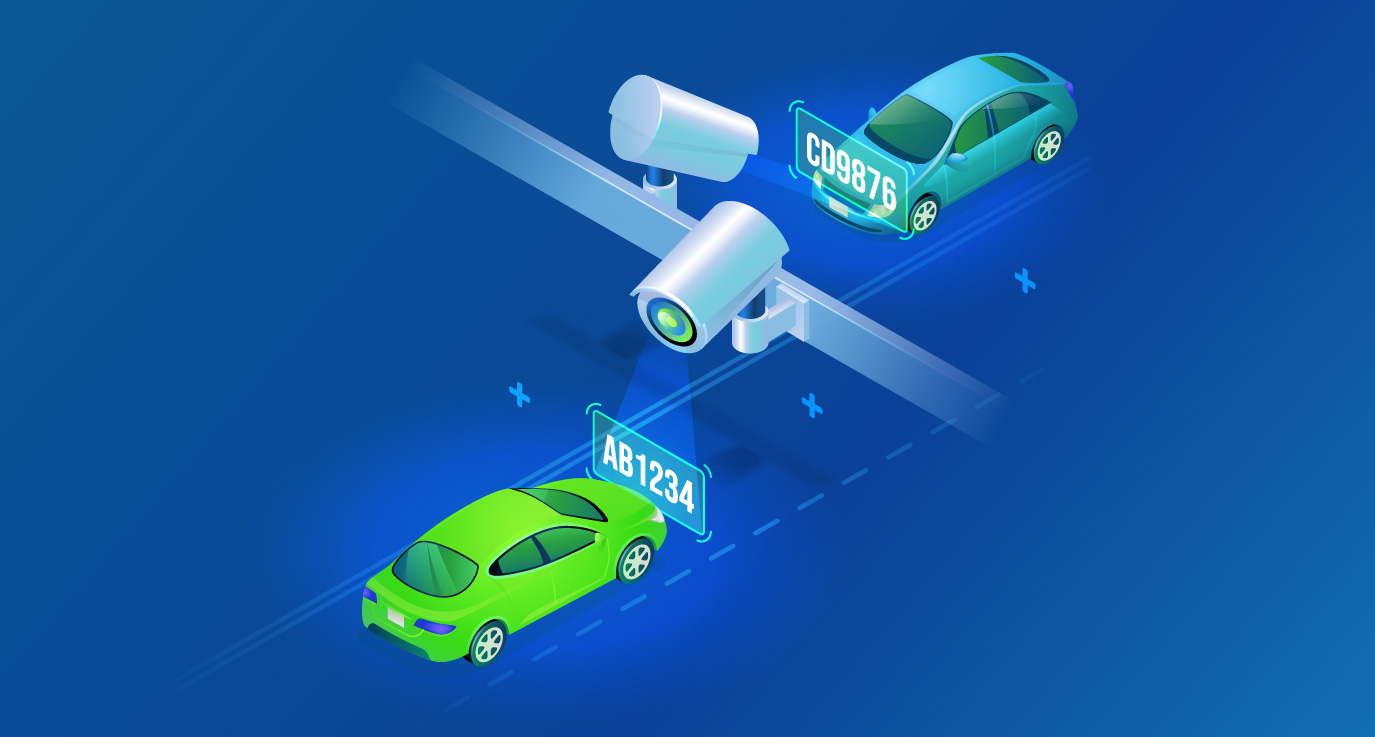

License Plate Recognition (LPR) systems, once the gold standard for tracking and security, have now become just one component of an increasingly intricate landscape. This shift can be attributed to the rapid advancements in technology and its implications for law enforcement agencies and criminals alike.
In the following sections, we'll explore the intricate world of vehicle tracking while we delve into why merely recognizing a license plate might not be enough in today's fast-paced world, especially as motorcycle crime and other sophisticated crimes are rising.
Table of contents
- What is license plate recognition (LPR)?
- Phases of license plate recognition (LPR)
- Types of license plate recognition technologies
- Industries using license plate recognition (LPR)
- Limitations of license plate recognition (LPR)
- The rise of motorcycle crime: A growing threat
- vehicleDRX: A revolution in suspicious behavior detection
What is license plate recognition (LPR)?
License Plate Recognition (commonly referred to as LPR) is a technology implemented in an Intelligent System that allows cameras to detect and capture images of license plates in diverse vehicles such as motorcycles, cars, trucks, or trailers.
In a world with nearly one and a half billion vehicles as of 2023, the automatization of plate recognition is pivotal to keeping some record and order in the streets, highways, or parking lots.
LPR gathers the images from live or recorded feeds and transforms the information into data that can be run through databases for several purposes, such as security, law enforcement, traffic control, or parking efficiency.
This technology allows for a plethora of useful information to be gathered from an image or video, such as the time, place, direction, or speed of a vehicle. It also can help identify the model of the vehicle, its origin, or if it is listed with any security alert. Additionally, this data can help pinpoint other useful information, such as the driver’s name, license number, and any contact information about the driver in the databases available.
To make LPR more accurate, the algorithm that controls it can be trained to read only specific plates (for example, only of a single state), or it can be trained to recognize plates from all around a country, which means discerning between diverse fonts, colors, designs, or sizes.
As can be seen, much information can be gathered from and fed to a system enhanced with LPR. The type and amount of data gathered will depend on the purpose of the LPR; for example, while a police camera might gather the license number and name of the driver of a suspicious car, that information might not be relevant for a parking lot camera.
Phases of license plate recognition
Although License Plate Recognition can seem an immediate affair, it is, in truth, a process with different stages, each one with a particular function that results in all the data mentioned above. We will explain the four phases of LPR needed to work accurately and efficiently.
Localization
The first part of the process after the camera captures the image of a passing or stationary car is localization, which entails using algorithms to pinpoint the location of the license plates in an image.
This might seem like an easy task, but the system must automatically disregard any unnecessary data in the image (like other objects with text in them) while also recognizing the shape or size of the plate to determine accurately that it is indeed a plate.
Segmentation
Once a license plate has been accurately located in an image, LPR systems have the task of segmenting the characters within the plate. This means that the algorithms must recognize the specific zone that contains each character within the plate. This ensures that every single character can be clearly and accurately read.
Identification
This entails the actual process of recognizing the characters in each zone previously segmented. This step makes it possible to get the complete license number of a vehicle. With this, the data is almost ready to be sent to the database for an accurate recognition of the plate. However, a last step is necessary.
Regionalization
This final phase in the License Plate Recognition process ensures no ambiguities in characters that might be identical according to the region the plate belongs to.
Using Regional Syntactical Correction, the characters identified in the previous step are confirmed as I instead of 1s, Os instead of zeroes, and Bs instead of 8s, among other possible confusions.
Types of license plate recognition technologies
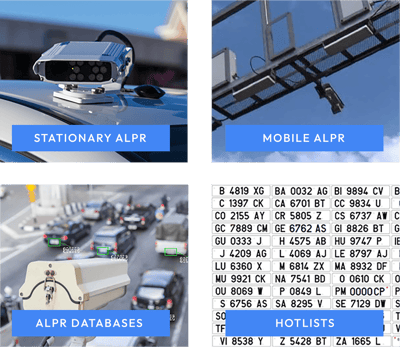
License Plate recognition uses different technologies to gather information from images and videos.
At the same time, different kinds of devices or databases are required for specific tasks. In this section, we will explain the most important technologies used by LPR, from cameras to special databases.
STATIONARY ALPR
Automated License Plate Readers are the camera systems that usually gather the images and footage to begin the LPR process. Stationary ALPRs, as their name might suggest, are cameras located in a single location that cannot be moved around. They might be installed in specific places like traffic lights, facility gates, telephone poles, highway toll booths, or parking lots.
They are usually connected to a central system that gathers information from other stationary ALPRs in a certain place to extrapolate data such as the direction and speed of a car. Several ALPR cameras might work together to monitor a single place and to keep it safe or controlled. These are also essential for traffic control on streets or highways and law enforcement in the cities.
MOBILE ALPR
These types of cameras can be moved from one place to another to read the license plates of cars on the road or during emergent events with no stationary cameras installed (for example, car races or music festivals).
Mobile cameras are often used by patrolling officers, which turn them on at the beginning of a shift to access relevant information immediately in case a car is involved in a crime or a traffic infraction is being committed.
This recent technology has helped law enforcement recognize license plates faster and more efficiently, saving time and effort while keeping officers and citizens safer.
ALPR DATABASES
Like all the technologies enhanced with AI, ALPR cameras have access to databases that gather information from a wide range of sources. As soon as a plate is correctly identified, it might be run against a database to obtain relevant data regarding the driver or the vehicle.
These databases might be private or public. For example, ALPR cameras belonging to the police might use a database with the public records of a car or its driver.
On the other hand, private ALPR cameras in a parking lot can gather information about certain cars and check in the database if the vehicle has access to a certain parking area during a specific time.
HOTLISTS
Hotlists are a specific type of database mostly used in security and law enforcement matters. These hotlists include license plates of interest that ALPR systems will flag in case they recognize them.
These listed plates can belong to stolen vehicles, vehicles involved in a crime, or even vehicles with expired registrations. An alert will be sent to the system, and the officers will be notified immediately, reducing their response time significantly.
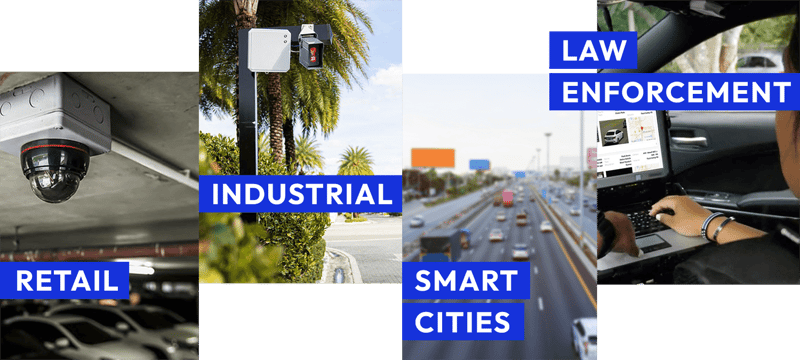
Industries using license plate recognition (LPR)
License Plate Recognition has become an essential technology in several industries worldwide due to its benefits to security, traffic control, and vehicle detection.
In this section, we will explore how License Plate Recognition has been used by some industries and the benefits it provides.
Retail (Parking)
LPR can be implemented in the parking lots of Retail Stores. The parking operation can be automatized and enhanced by detecting the flux of vehicles in and out of the store’s premises. Access to certain vehicles can be granted or denied remotely without the need for a security booth.
Additionally, LPR could help the store better control the parking spaces while also gathering accurate statistics of hours in which there are more customers, the time spent in the store, and the frequency in which a certain car visits, among other useful data.
Industrial (Quality Control)
License Plate Recognition can be used in industrial plants to keep a register of product providers or other cars entering the premises.
Flags can be sent to the system every time a product provider arrives or leaves the parking spaces, which helps to have better control of the spaces and of the delivery schedules. This often results in an efficient and seamless delivery.
Smart Cities (Traffic Control)
Smart cities are urban areas that have implemented a complex system of technologies to enhance and ensure the proper working of certain services such as security, public lighting, and public transportation.
LPR has proven to be essential for traffic control within these cities since it can monitor traffic flow in certain streets and, at the same time, identify vehicles involved in accidents to send alerts to the proper authorities.
Outside of the cities, LPR can also help collect tolls by identifying the cars using the highways or roads and automatizing the process.
Law Enforcement (Vehicle detection)
License Plate Recognition has been a game-changer in law enforcement and public security matters. Police departments have been using intelligent systems with LPR to detect in real-time plates of vehicles of interest, such as stolen, wanted, or uninsured vehicles.
Using the network of stationary or mobile ALPR cameras spread throughout the city, the command centers can monitor the streets 24/7. This has helped reduce the number of total or partial thefts of vehicles and has also made it possible to detect and follow any vehicle being used as a tool for committing a crime.
In this way, LPR can help law enforcement create safer cities and protect vehicles, which are a necessity for many people worldwide.
4 INDUSTRIES USING LICENSE PLATE RECOGNITION (LPR)
Limitations of License Plate Recognition (LPR)
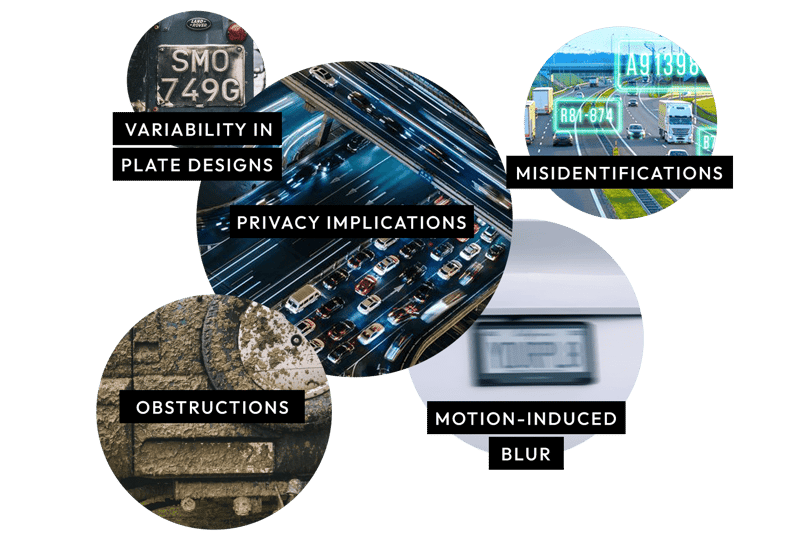
While License Plate Recognition (LPR) brings numerous advantages to the table, it's far from foolproof. Relying exclusively on this technology in our ever-evolving society and the multifaceted threats it faces has its pitfalls.
Here are some inherent challenges with LPR systems:
Environmental Conditions
LPR systems can falter under varying light conditions. Nighttime or overcast days may hamper the clarity of captured images. Additionally, inclement weather, such as intense rain or snowfall, can cloak the license plate, hindering the system's ability to decipher it.
Obstructions
Elements like dirt, mud, or other forms of debris can obscure plates. Even a slightly concealed plate can derail the system's accuracy.
Motion-Induced Blur
Motion blur presents a challenge, especially pertinent to mobile ALPRs or vehicles zooming by at high velocities. Capturing a crisp image becomes an uphill battle with the sheer speed of some vehicles.
Variability in Plate Designs
License plates aren't standardized globally. Their designs vary greatly, with regions or countries presenting unique fonts, colors, and layouts. LPR systems must be versatile enough to accommodate this vast diversity.
Misidentifications
Despite their efficiency, LPR systems are not immune to errors. Occasionally, they produce false positives, misconstruing a plate number or misinterpreting a character.
Privacy Implications
There's a thin line between surveillance for safety and infringement of privacy. The extensive data LPR systems amass can be a double-edged sword. This information could compromise individual privacy in the wrong hands or without proper regulation.
In light of these challenges, it becomes imperative to continuously refine and complement LPR systems to ensure they serve their purpose effectively and adequately respond to critical modern threats, like motorcycle crime.
LIMITATIONS OF LICENSE PLATE RECOGNITION (LPR)
The rise of motorcycle crime: A growing threat
Motorcycle crime present a unique challenge for LPR systems since they cannot help law enforcement agents address and react to this problem.
Recent trends have witnessed a surge in motorcycle-related crimes, notably within Latin American regions.
Motorcycles are often targeted due to their size, ease of theft, and the speed at which they can evade capture.
These are some of the reasons why motorcycles are increasingly being used to commit crimes, which directly affect the efficiency of license plate recognition (LPR) systems:
- Size and Position: The license plates on motorcycles are generally smaller and sometimes positioned in a way that might be harder for cameras to capture, especially from a distance or specific angles.
- Speed: Motorcycles can easily maneuver through traffic and can quickly accelerate, making it challenging for LPR systems to get a clear capture of their license plates.
- Use in Crimes: Their agility and speed make motorcycles preferred for crimes like snatch thefts. Their ability to quickly escape and blend makes it essential for LPR systems to adapt and improve.
Addressing this requires a shift in focus towards the nuances of motorcycle-driven crime behaviors and innovating technology to proactively identify, alert, and aid law enforcement in timely responses.
If you want to learn more about Mexico's crime problem and its impact in Mexico, visit our article on Homicides, armed robberies, and robberies: the most common crimes committed on motorcycles in Mexico and the role of AI video surveillance.
vehicleDRX: A revolution in suspicious behavior detection
vehicleDRX is the next step in vehicular monitoring since it’s the only product in the world capable of identifying suspicious behavior on motorcycles and also search and track autonomously any vehicle interest.
In other words, while LPR focuses on license plates, vehicleDRX goes further by focusing on behaviors and patterns, leveraging all the available technology.
These are some of the advantages that vehicleDRX has over license plate recognition (LPR) systems:
- Behavioral Analysis: VehicleDRX can analyze the behavior of a vehicle, noting patterns or suspicious activities. For instance, if a vehicle is found loitering in a particular area or is spotted at the scenes of multiple incidents, VehicleDRX can flag it.
- Plug and play technology: Adapts to any video surveillance network in a command center.
- Autonomous tracking of vehicles of interest
- Advanced Algorithms: The technology uses sophisticated algorithms to differentiate between normal and suspicious behavior, ensuring fewer false positives and more accurate threat detection, and most importantly, without relying on that bitch, LPR
- Real-time Alerts: In situations requiring immediate action, VehicleDRX can send real-time alerts to the concerned authorities, enabling quicker response times.
- Capability of sharing information with third entities, according to the privacy policies of each entity.
With vehicleDRX, the future of vehicle safety looks bright as it ensures safer and smarter cities, evolving current technologies to achieve maximum productivity in critical industries.